Changelog 0.8 alpha 7 (en)
General
Upgrade to Python 3 (3.11 to be exact) and Wxpython 4 (4.2.2): thanks to Laurent Mérat for doing most of the work!
The software is compatible with the latest versions of R (4.4.1 for the moment): it is advisable to use it with the latest version available at the time of installation on Mac and Windows.
Iramuteq should find the version of R installed on all systems on its own.
Analyses can be exchanged between systems (an analysis performed on a Mac will open on Windows or Linux and vice versa).
Three new R packages are installed: sna, network and intergrpah.
Configuration files are now in a folder with the version number (.iramuteq-08a7 for example).
Numerous bugs have been fixed and many more are likely to be introduced :)
Windows
The Windows version is now 64 bit.
The installation folder includes the version number: it is therefore possible to have several versions of iramuteq on the same machine.
The software should work regardless of system encoding.
A version of R >= 4.4.1 is required.
All intermediate files and results are now encoded in utf8.
Analyses performed with the previous version are not compatible (text and matrix).
Mac OS
This version runs on the latest version of Mac OS (15.0.1 and earlier).
There's now a version for Macs with Intel processors and one for those with Apple processors (M1, M2, M3 and more...).
Interface
Font size now selectable (Edit -> Preferences)
Searchable list of indexed corpora (Ctrl+F in history)
Text indexing
It is now possible to define a default language for texts (Edit -> Preferences)
Corrections have been made to most dictionaries to eliminate situations where the same lemma appeared with two (or more) different grammatical categories.
Addition of several languages: Dutch, Galician, Norwegian.
New analyses
On texts
- Back to full text
In all analyses, concordancers now display a link at the end of the starred line. Clicking on the link opens a window containing the full text from which the segment was taken. The segment concerned appears in red in the text.
-
Labbé distances
Calculates Labbé distances based on whole lexical tables. This analysis uses the same dialog as the Specificity and CFA analysis. The user selects a variable or modalities and the distance matrix between the parts concerned is calculated. The results are displayed in the form of a tree representing a Ward classification on the distance matrix, a HeatMap graph, a colored representation of the matrix and a list of all distances. The matrix is exported in a csv file.
The calculation of this distance was proposed and described by Dominique Labbé in the following articles:
Labbé, D., & Monière, D. (2000). La connexion intertextuelle. Application au discours gouvernemental québécois. In M. Rajman & J.-C. Chappelier (Eds.), Actes des 5èmes Journées Internationales d'Analyse statistique des Données Textuelles, Lausanne: EPLF, 85-94.
Labbé, C., & Labbé, D. (2003). La distance intertextuelle. Corpus, (2): 95-117.
An example of the application of this analysis in iramuteq for crossing classifications is proposed in this article:
Ratinaud, P., & Marchand, P. (2016). Quelques méthodes pour l’étude des relations entre classifications lexicales de corpus hétérogènes : application aux débats à l’assemblée nationale et aux sites web de partis politiques. In D. Mayaffre, C. Poudat, L. Vanni, V. Magri, & P. Follette (Eds.), Statistical Analysis of Textual Data (pp. 193-202). http://lexicometrica.univ-paris3.fr/jadt/jadt2016/01-ACTES/83670/83670.pdf
- Corpus based on classes
This is not really an analysis. It's a tool for reconstructing corpora from classes derived from any Reinert classification, even on different corpora. Simply browse the tree of corpora and analyses and select the classes you wish to combine. They are named automatically (configurable) and the metadata is added to all segments of the class. The list of selected classes is displayed in the right-hand window.
The resulting corpus can be used to perform CFAs or Labbé distance analysis on the classes.
This approach is illustrated in the following articles:
Ratinaud, P., & Marchand, P. (2016). Quelques méthodes pour l’étude des relations entre classifications lexicales de corpus hétérogènes : application aux débats à l’assemblée nationale et aux sites web de partis politiques. In D. Mayaffre, C. Poudat, L. Vanni, V. Magri, & P. Follette (Eds.), Statistical Analysis of Textual Data (pp. 193-202). http://lexicometrica.univ-paris3.fr/jadt/jadt2016/01-ACTES/83670/83670.pdf
Ratinaud, P., Smyrnaios, N., Figeac, J., Cabanac, G., Fraisier, O., Hubert, G., Pitarch, Y., Salord, T., & Thonet, T. (2019). Structuration des discours au sein de Twitter durant l’élection présidentielle française de 2017 : entre agenda politique et représentations sociales. Réseaux, 2019/2-3(214-215), 171-208. https://doi.org/10.3917/res.214.0171
On matrix
- ElCaTeGoRiZaToR
This is a categorization tool. It was originally designed to categorize responses to verbal associations, but can be used to categorize any type of open-ended question, or to produce groupings of modalities on closed questions or scales. The analysis is carried out in three stages:
First, select the column(s) of the matrix you wish to categorize;
An interface with three columns appears:
- The left-hand column contains all the different shapes to be categorized, with their numbers;
- The middle column is initially empty. It will contain the categories created (and their numbers);
- The left-hand column shows the contents of the selected category, and their numbers.
To create a category, you can either drag and drop items from the left-hand column into the middle column, or click on the “Add category” button;
To add an element (or several) to an existing category, select it (or them) and drag the selection onto the target category, or into the right-hand window if the category is selected.
Categories can be renamed (double-click on the category name);
Changes are not saved automatically: it is therefore essential to click regularly on the “Save” button.
The “Export columns” button exports categorized columns in the order of the original file;
The “Import categorization” button lets you reuse a previous categorization on a new dataset;
The “export dictionary” button exports the category dictionary (list of categories with their numbers, the elements they contain and their respective numbers).
- McNemar Chi2
Offers a McNemar chi2 (for paired data) on 2x2 tables (by crossing 2 columns each containing a 2-modality variable).
New in analyses
Reinert classification (text)
New chronological visualization in class profiles (right-click in profile -> Chronological visualizations).
How to read these analyses is described in the following article:
Ratinaud, P. (2014). Visualisation chronologique des analyses ALCESTE : application à Twitter avec l’exemple du hashtag #mariagepourtous. Actes Des 12eme Journées Internationales d'Analyse Statistique Des Données Textuelles (JADT 2014), 553-565. http://lexicometrica.univ-paris3.fr/jadt/jadt2014/01-ACTES/46-JADT2014.pdf
These visualizations can also be used on non-chronological metadata ;)
Spiral: new placement algorithm for word graphs.
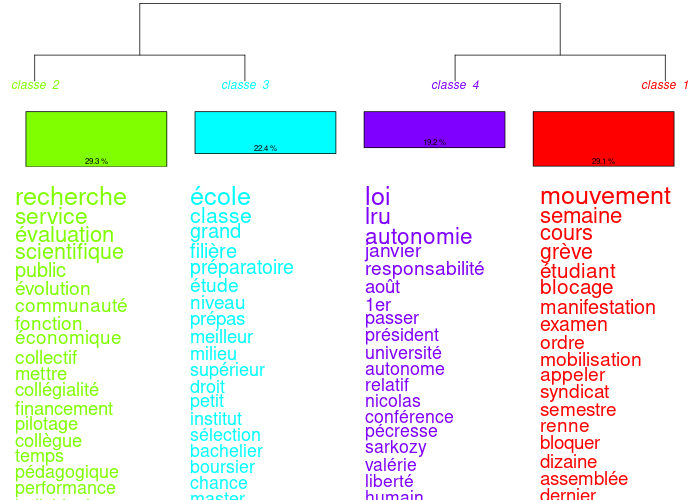
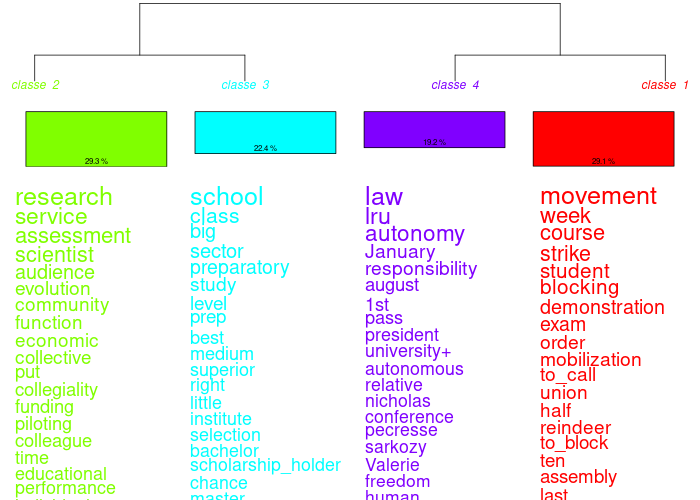
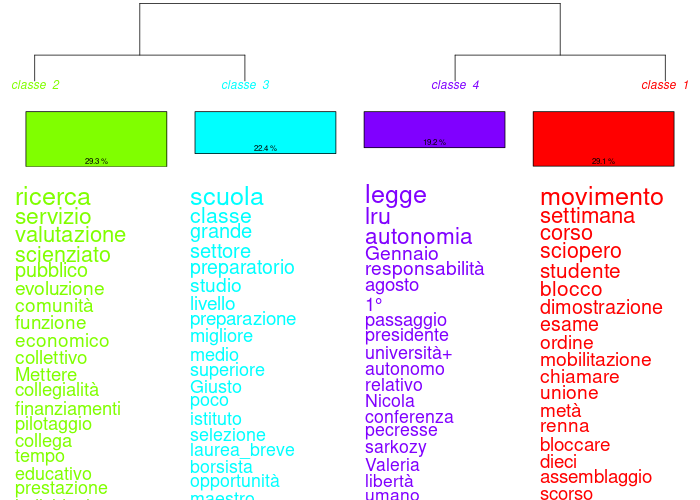
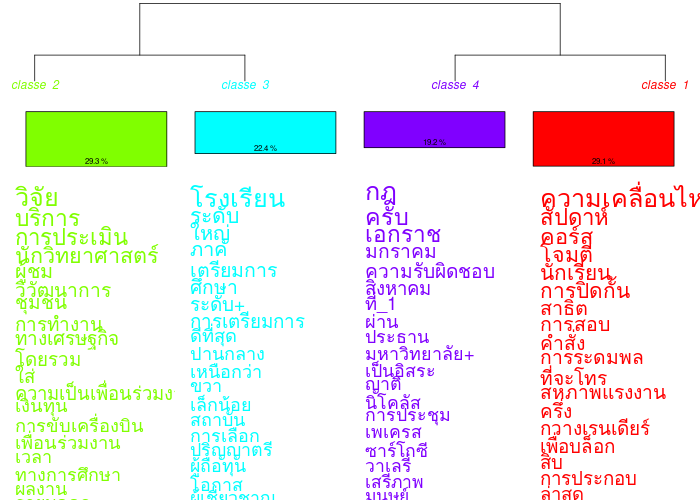
Profile translation (right-click on a classification name in the history): a tool for translating class profiles (max. 50 shapes per class + max. 50 additional shapes) has been added. It uses a free API from google and offers word-for-word translation. When abused, google blacklists your IP and you can't access the API for x days. You've been warned ;) You can correct the translation in the results files. You get the profiles in the new language. You can use this translation in the dendrograms in the “CHD” tab.
In the following example, the analysis was performed on a French corpus and translated into English, Italian, Greek and Thai:
Characteristic segments by class (right-click on a classification name in the history): produces characteristic segments for all classes in a classification.
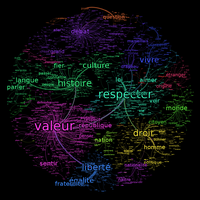
Similarity analysis
The Frutchterman-Reingold placement algorithm (default choice) now comes from the sna package. The result is much easier to read than before.
By default, only the first 200 words are selected.
Edges are straight by default.
Added a button to export the similarity matrix. WARNING: these matrices can be huge.
Specificities and CA
A new tab presents statistics by column (occurrences, number of forms, number of texts, etc.). The hapax count is based on the hapax of the complete corpus.
Actions sur le document